How common are sexually inactive marriages? You might not really want to know the answer, but it’s not that bad. Just 2% to 16% of married couples fall into this category. From health to habit, a variety of things end up taking sex out of the bedroom.
Below we’ll unpack how often and why this happens, providing insight without oversimplifying the personal and complex nature of this unexpected situation.
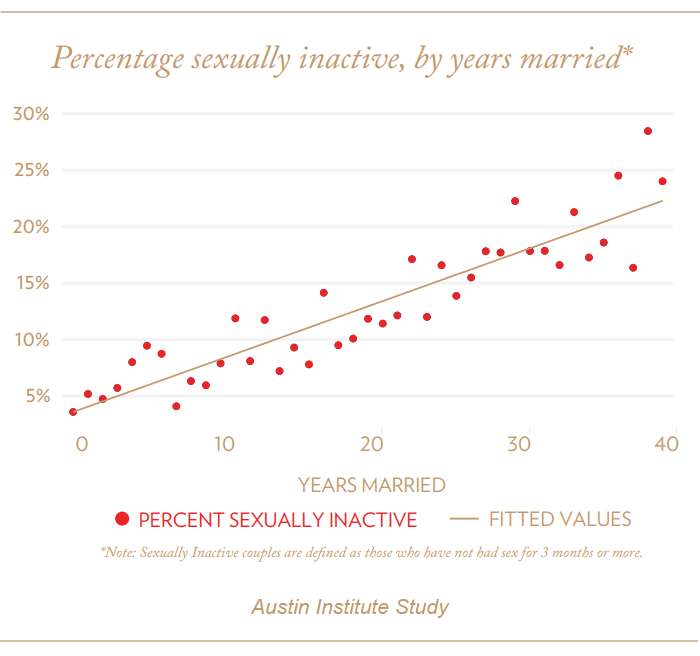
Prevalence of Sexually Inactive Marriages
What is a “sexually inactive” marriage, anyway? It is one where the partners do not pleasure each other physically in a sexually gratifying way. That’s a mouth full (no pun intended).
In other words, if you perform oral sex on each other, use aids like sex toys, or give each other physical sexual pleasure in other ways, you are not “sexually inactive.”
How long does it take for a marriage to be sexless? Experts disagree, but the most common definition seems to be when there are less than 10 instances of sexual activity during a 12-month period.
A marriage without sexual activity is relatively unusual. Dr. Laura Vowels points out that about 2% to 10% of marriages are considered sexless. An examination of data from the U.S. shows that nearly 16% of married couples were sexually inactive in the month prior to the study. This means that the statistic is 2-10% usually, but in that one prior month in the study, it happened to be 16%.
For whatever reason, many American adults adopt sexual inactivity as a long-term lifestyle. A significant number of individuals experience extended periods of no sexual activity, lasting up to five years or beyond.
This suggests that sexual frequency in marriages is influenced by a variety of factors, and achieving a sexually active life could be dependent on addressing and fixing these obstacles.
Sociodemographic Factors
Sociodemographic elements like age, marital status, and race significantly influence the occurrence of sexless relationships. For instance, sexlessness is higher in:
-
Females
-
White people
-
The elderly
-
Currently unmarried individuals
-
Those who are religiously observant
-
Those with a lower socioeconomic status
Gender Differences
Overall, whether married or unmarried, studies show that women are more likely to report a lack of sexual activity compared to males. Make sure to take note of the word “report.”
It’s pretty well-known that women generally underreport when it comes to their “numbers” or “body count,” meaning the number of people they have slept with. Underreporting makes them seem more in line with traditional gender roles of women saving themselves for marriage and being pure and Biblical.
Men typical overreport because a high number conquests (women they have “conquered” by having sex with them) enhances their manliness.
But inside a marriage, both genders report similar rates of sexlessness in the U.S. This suggests that the phenomenon of sexless marriage is not limited to one gender but affects both men and women broadly. And both men and women see a sexless marriage as a bad thing. They consider sex to be an essential part of a healthy marriage.
Likewise, both men and women generally refuse to have sex with their spouses at the same rates.
Causes of Sexless Relationships
Deciphering the reasons behind sexless relationships is like piecing together a complex puzzle. Broadly, the causes can be attributed to physical health concerns, emotional and mental health factors, and communication challenges. Each of these elements intertwines and interacts in intricate ways to influence sexual desire, frequency, and satisfaction within a relationship.
Physical Health Concerns
Numerous physical health issues commonly pose a significant obstacle to sexual activity. Here are some of the most common chronic health conditions that decrease libido and cause sexual dysfunction:
-
Depression
-
Joint, muscle, or back pain
-
Cancer
Even seemingly minor health issues like back, joint, or muscle pain can have a profound impact on a couple’s sex life. When someone is in pain, sex needs to be more planned so that the couple can try to have sex in a manner that minimizes the pain.
A couple will naturally have less fun when they have to be careful about how and how long they are having sex, as well as lessening their exploration of sexual fantasies, making them have sex less frequently and altering the types and manner of sex that they previously enjoyed with each other.
When there is a health problem, it can be the health condition itself that is interfering with a healthy sex life, but it can also be the side effects of the prescribed medications.
For instance, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) can make it difficult to get and maintain an erection and orgasm. Tamoxifen, which is an anti-cancer drug for people who have had cancer, often results in vaginal dryness, which makes sex uncomfortable without proper lubrication.
Physical health concerns, if left unaddressed, can often lead to a gradual decline in sexual activity, resulting in a sexless marriage.
Emotional and Mental Health Factors
Ever heard the joke: Go ahead and put a penny in a jar for every time you have sex before marriage with your mate. Then, take one penny out of that jar for every time you have sex after the two of you get married. You will never take all those pennies out of the jar.
If this is you, it could be because you or your spouse’s emotional bank account isn’t full enough to want to have sex. You can research how to fill your spouse’s emotional bank account. There are all kinds of theories about what to do to keep your marriage healthy, but in short, if you or your partner aren’t feeling (emotions) good about each other, you are not going to want to have sex with each other.
Then there is the baggage that gets in the way. Past experiences, such as sexual abuse, can evoke emotional responses like fear and shame, post-traumatic stress, and distortions in self-perception. Stress, in particular, can reduce libido and lead to difficulties in getting or sustaining an erection. High stress levels can also cause distractions that make it hard to be in-the-moment and fully present while having sex, leading to a less-than-stellar romp in the sheets.
Physical issues can become emotional issues. For example, if a person is disfigured, whether from birth or accident or surgery (such as some types of mastectomies), they can feel unattractive and thus less likely to initiate and enjoy sex because of how they feel about their own appearance.
Emotional maturity in an individual is commonly an obstacle in communicating about sexual needs and desires, and also an obstacle in overcoming any impediments such as erectile dysfunction. Each of these can significantly influence the frequency and quality of intimacy, as well as sexual desire in a relationship.
Mental health conditions, including depression and substance abuse, along with certain medical conditions like diabetes and hypertension that have low sexual desire as a side effect, can all contribute to decreased sexual activity in a relationship.
Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD), which is a mental health condition where the person overly worries about their physical flaws, can also be a contributing factor.
Communication Challenges
When couples don’t communicate well, it can lead to probems in the bedroom. It could be a lack of communication in general that ends up hurting the marital dynamic, or it could be communication about sex.
When problems with communication lead to unresolved conflicts in a marriage, sexual activity usually suffers. Minor disagreements become significant arguments and end up damaging the relationship.
Insufficient communication can be due to emotional immaturity or unavailability, but it could also be from embarrassment or growing up in an environment where sex was a taboo subject.
Whatever the cause, inadequate communication about sexual matters significantly decreases a partner’s sexual desire for their partner (though not necessarily decreasing their sexual desire generally).
It also lessens how aroused that person is during sex, which has the physiological effect of diminished lubrication, difficult or nonexistent orgasms, and erectile dysfunction. Interestingly, the impact of poor communication on sexual desire and arousal is generally stronger in married individuals compared to those who are dating.
The communication challenges that often lead to less sex in marriages include:
-
Inadequate sexual communication about wants and needs
-
Trust issues, either related to sex or completely unrelated to sex
-
Built-up resentment from things that have happened in the relationship over time
-
Struggles with vulnerability, which may have been caused inside of the marriage or unrelated to the marriage
-
Financial conflicts between the couple
Addressing these issues is necessary for a couple to truly communicate and once again light their sexual fire.
Coping with Sexual Inactivity in Marriage
Once we take the first step and understand the causes of sexual inactivity in marriages, we then need to take the next step of dealing with it.
Below we’ll look at how fostering emotional connection, enhancing sexual communication, and understanding sexual attraction can significantly improve sexual satisfaction and the overall relationship quality.
Fostering Emotional Connection
Sexual intimacy is just one aspect of a relationship. Emotional intimacy is needed as well and is vital to maintaining a relationship. Being able to talk to each other about deeply personal feelings and thoughts, free of judgment, deepens your bond, helps you be happier with each other, and creates positive and intimate feelings for each other.
When a marriage is sexless, the couple’s communication and emotional bonds almost always deteriorate. When a couple does not have emotional intimacy, they typically will have less sex. Whichever happens to come first in any particular situation, the couple becomes more distant from each other. Each has an intensified feeling of solitude, seclusion, and emotional anguish, ultimately weakening their relationship.
When this happens, it is critical for couples who want their relationship to last to actively foster an emotional connection through shared values, goals, and experiences.
Enhancing Sexual Communication
To address sexual inactivity in a relationship, effective sexual communication is essential. It involves:
-
Having realistic expectations of what is going to happen and what you are going to get out of sex with your partner.
-
Obtaining consent for having conversations, in confidence and free of judgment.
-
Revealing your desires, interests, boundaries, and concerns openly and honestly, including what turns you on and what you would like to try during intercourse and other types of sexual activity.
-
Discussing how to satisfy the sexual desires and interests of your partner in a way that is safe and that you feel comfortable. This should include agreeing on a “safe word” which is a word (like popcorn, canary, or anything totally out of place) that tells your partner that you are not comfortable and the activity needs to stop.
By following these steps, couples can significantly improve sexual communication, including discussing preferences in oral sex.
Both parties must feel safe in order to truly enjoy the sexual experience. To feel safe, it’s important to discuss boundaries. You must be very clear about what you don’t want to do and what doesn’t feel good. Just as an example, if someone likes to pat your bottom and tends to be too rough, you need to be clear that when the pat becomes a slap, that it hurts you, you don’t like it, and it doesn’t turn you on.
Seeking Professional Help
Occasionally, couples may require professional assistance to address sexual inactivity in their relationship, despite their best efforts. A sex therapist can assist couples in clarifying their needs, enhancing communication, and reigniting intimacy within a sexless marriage.
They provide valuable guidance and support, helping couples navigate the complexities of their sexual relationship.
Couples therapy addresses sexual inactivity in marriages by assisting couples in resolving issues related to trust, vulnerability, and communication that could be impacting sexual intimacy. When seeking a professional counselor, consider qualifications such as a master’s degree in counseling or a related field, completion of a supervised clinical experience, and state licensure.
Seek a counselor who specializes in working with couples and who also has experience in addressing intimacy and relationship issues.
Impact of Sexless Marriages on Relationship Satisfaction and Happiness
Sexless marriages can have a wide-ranging impact on relationship satisfaction and happiness. For some individuals, the lack of sexual activity can lead to feelings of disconnection from their partner and frustration with the marriage. Although the presence or absence of sexual activity is just one aspect of overall well-being, it is an important one.
Relationship Satisfaction
There is a close connection between sexual activity and relationship satisfaction. In a Pew Research Center survey, 61% of respondents highlighted the significance of a fulfilling sexual relationship for a successful marriage. This finding emphasizes the value placed on intimacy within a healthy marital relationship.
When a couple is not having sex, there is typically an increase in tension and a decrease in a feeling of closeness. From here, they tend to have more negative emotions towards each other, which increases conflict and leads to unhappiness. This leads to divorce.
Clearly, maintaining a satisfying sexual relationship has a direct and significant effect on the quality of the marriage and how long it lasts.
Self-Reported Happiness Levels
Numerous factors complicate the correlation between sexual activity and self-reported happiness levels, and studies have found that the correlation is inconsistent.
After accounting for certain variables, females who are unhealthy did not show a connection between sexlessness and happiness levels. Similarly, males in sexless marriages did not show a decreased level of self-reported happiness.
However, individuals who report a more active sexual relationship also report greater happiness within their marriage, indicating that for some individuals, the frequency of sexual activity can enhance marital happiness.
Alternative Perspectives on Sexless Marriages
Beyond focusing on the challenges and impacts of sexless marriages, it’s vital to take into account different viewpoints. Some couples consciously choose to have a sexless marriage, valuing other forms of intimacy and connection over sex. This challenges societal expectations around sexual activity in relationships and emphasizes the importance of individual preferences and needs.
Consensual Sexless Marriages
In a “consensual sexless marriage,” both partners mutually agree that sexual intimacy is not a priority. These types of marriages are more prevalent than one might anticipate, with estimates indicating that they make up approximately 15% to 20% of couples. In the U.S., surveys indicate that around 7% of married adults are in consensual, sexless marriages.
On the other hand, a “sex-starved marriage” is a situation where one or both partners desire sexual intimacy but are not experiencing it.
The success of consensual sexless marriages can be attributed to various factors, including:
-
Navigating differences in sexual desire
-
Effectively managing common issues such as health complications, mismatched libidos, childbirth, stress, and communication differences
-
Focusing more on other aspects of companionship, such as emotional connection through shared values, goals, and experiences
The takeaway is that there are functional marriages where the couple involved has decided that they find happiness and fulfillment with each other by doing a variety of non-sexual activities.
Challenging Societal Expectations
The societal norms and expectations concerning sexual activity in marriages can place unnecessary pressure on couples, particularly those in sexless marriages.
These societal norms have evolved over time, with contemporary perspectives generally emphasizing the expectation for women to be sexually accessible and responsive, and to fulfill these desires within the confines of their marriages.
However, such norms and expectations can create a fear of sexual relationships, stigmatize later life sexuality, overestimate peers’ sexual activity, and cause internalized shame among couples in sexless marriages.
Media and popular culture often perpetuate these norms and expectations, thereby reinforcing gender stereotypes and creating a skewed portrayal of sexual activity within marriages.
Once we understand and accept that sexual activity is neither a universal requirement for all couples, nor is it a universal desire by all couples, it is easier to explore and determine how to create happiness and satisfaction within our own marriage.
Sexless marriages, though less talked about, are more common than we might think. Various factors, from sociodemographic factors to physical health concerns, emotional and mental health factors, and communication challenges, can contribute to sexual inactivity in marriages.
Remember that sexual intimacy is just one aspect of a relationship. Other forms of intimacy and connection are equally significant.
While professional help can be beneficial, fostering emotional connection, enhancing sexual communication, and challenging societal norms and expectations can help couples navigate through the complexities of a sexless marriage.




